...
- Ready-made solution for working in the application;
- Multiple ways of interaction between host and application;
- Satisfies all conditions for taking snapshots on the host side without data corruption on the application side;
- Supported by QEMU;
- Availability in repositories;
- Easy to install and run.
Flaws:
- Requirements for running additional kernel modules and installing additional utilities on the application side.
- If the qemu-guest-agent is not running or listening to on the wrong cid when using VSOCK or chardev when using virtio-serial,
operations will not be available The inability for qemu-ga not to specify CID:Port. This possibility exists if we make our own utility. For this reason,
it is necessary to send information for the user (CID:Port) to the controller to configure qemu-ga on the application sideavailable. - No XEN support
How will it work?
...
-device vhost-vsock-pci
-device virtio-serial
In the first case, with -device virtio-serial, the guest agent is exposed to the host via a separate QEMU chardev
device (generally, a UNIX socket) that communicates with the agent using the QMP wire protocol (minus the negotiation)
over a virtio-serial or isa-serial channel to the guest. Assuming the agent will be listening inside the guest using
the virtio-serial device at /dev/virtio-ports/org.qemu.guest_agent.0 (the default).
Virtio-serial overview
- Virtio device for serial ports and console
- The host can add/remove ports
- Ports can be named (e.g. org.qemu.guest_agent.0)
- Guest agent opens /dev/virtio- ports/<name> character device
- The client app connects to QEMU chardev (UNIX domain socket, named pipe, etc)
...
Flaws:
- N:1 connections are clunky over the 1:1 serial port are not convenient and require an additional
a layer of abstraction to manage. This complicates the implementation of this functionality.- Applications have to multiplex over 1 stream
- Libvirt has to arbitrate access between qemu-guest-agent client.
- The relatively low number of ports available (~512)
- Limit is hard coded by the host
- Stream semantics (no message boundaries)
Ugly for datagram protocols
- Applications must use character devices instead of standard sockets API...Creating a new chardev on every App creation
-device vhost-vsock-pci
virtio-vsock is a a host/guest communications device. It allows applications in the guest and host to communicate.
This can be used to implement hypervisor services and guest agents (like qemu-guest-agent or SPICE vdagent).
Advantages:
- POSIX Sockets API so existing networking applications require minimal modification (unlike virtio-serial char devices)
- Listen to sockets Socket listeners (ex. Host) can accept connections from multiple clients (unlike virtio-serial char devices).
This allows you not to create a new chardev for each application for communication. - No address configuration setting is required inside in the guest No Ethernet or TCP/IP for a reduced attack surface for hypervisor servicessystem. The technology itself supports this functionality,
but apparently, qemu-ga has not yet been taught how to read system information from /dev/vsock at startup.
Although this is stated on the wiki page. Perhaps this will be corrected in the future. - Can be used with VMs that have no network interfaces
- An accessible library for Golang and very simple implementation on the EVE side.
Flaws:
- A hypervisor in EVE An application on that hypervisor with kernel 4.8+ (
- it is not actual for EVE)
- An application on that hypervisor with kernel 4.8+
- QEMU 2.8+ on the hypervisor, running the virtual machine The need to connect additional kernel modules on the application side
- possible for qemu-ga not to specify CID:Port when using VSOCK.
The documentation says that "No address setting is required inside the guest", but in practice this
does not work yet (Perhaps they will fix it in new versions). For this reason, it is necessary to send
information about (CID:Port) to the controller so that the user can run/configure qemu-ga on the application side.
Or we can use a mirrored CID, which will be equal to the TCP port. (For example 5891,...,n).
Thus, the CID will always be similar to the port and there will be no need to send additional information to the controller.
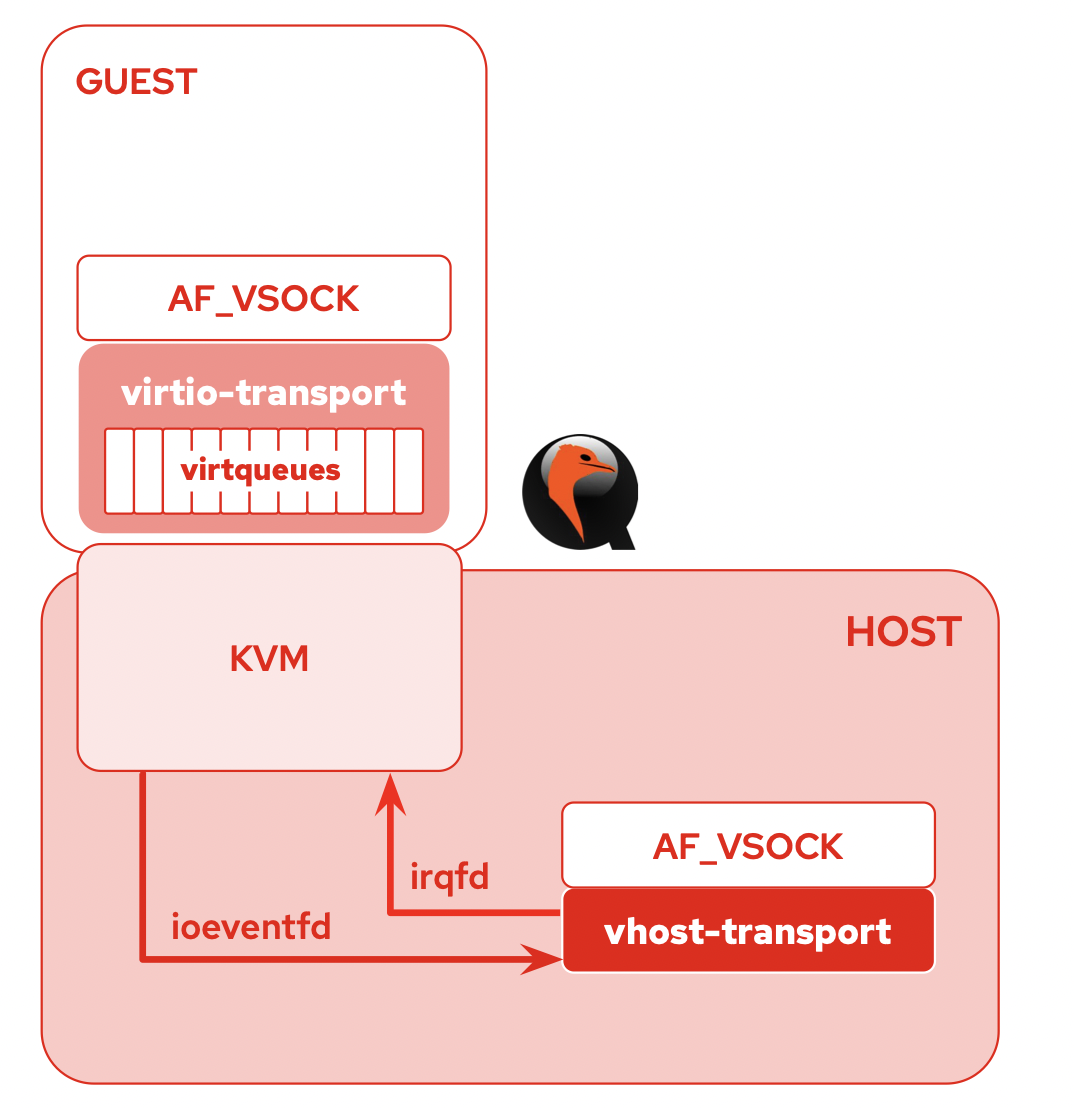
vhost-vsock-pci overview
Sockets are created with the AF_VSOCK address family. The SOCK_STREAM socket type is currently implemented for in-order,
guaranteed guaranteed stream semantics.
In EVE, we plan to implement exactly this method of communication with applications.
The proposed implementation of the functionality on the EVE side for working with snapshots.
...
These features will also use synchronization between EVE and the VM to guarantee command execution.
In addition, each of these functions will return the result of the command from the application
This functionality does not require sending any information to the controller, so the API in EVE will not change.
Suggested workflow for working with snapshots
...