...
- A new device state, “Unknown Update Detected” (Abbreviated as UUD) will be introduced in EVC, to indicate to in EVC that software running on a given device is not one of the intended/certified images
- An optional feature, "Location-Lock" may be introduced in EVC, to additionally check the Geo-Location reported by device, and flag if the location has changed since its last-seen location. This feature may be critical in some deployments, where a given EVE node may be mounted permanently, and any change in its physical location should be flagged, and optionally considered along with software measurements to conclude if the EVE node is trusted. In this regard, another new device flag, “Unknown Movement Detected” (Abbreviated as UMD) will be introduced in EVC, to indicate that a change in the location of the device has been detected.
- EVC maintains a central database of all the supported EVE software images, and their hash values, indexed with the EVE image version tag
- EVC also maintains a central database of mostly used BIOS firmware images, their signatures, and the certificate provided by the BIOS vendor for validating the signatures, indexed by a combined tag of BIOS version string + Manufacturer
- On every reboot, EVE sends PCR quote to EVC, along with optional Geo-Location information, along with its EVE image version and BIOS firmware version.
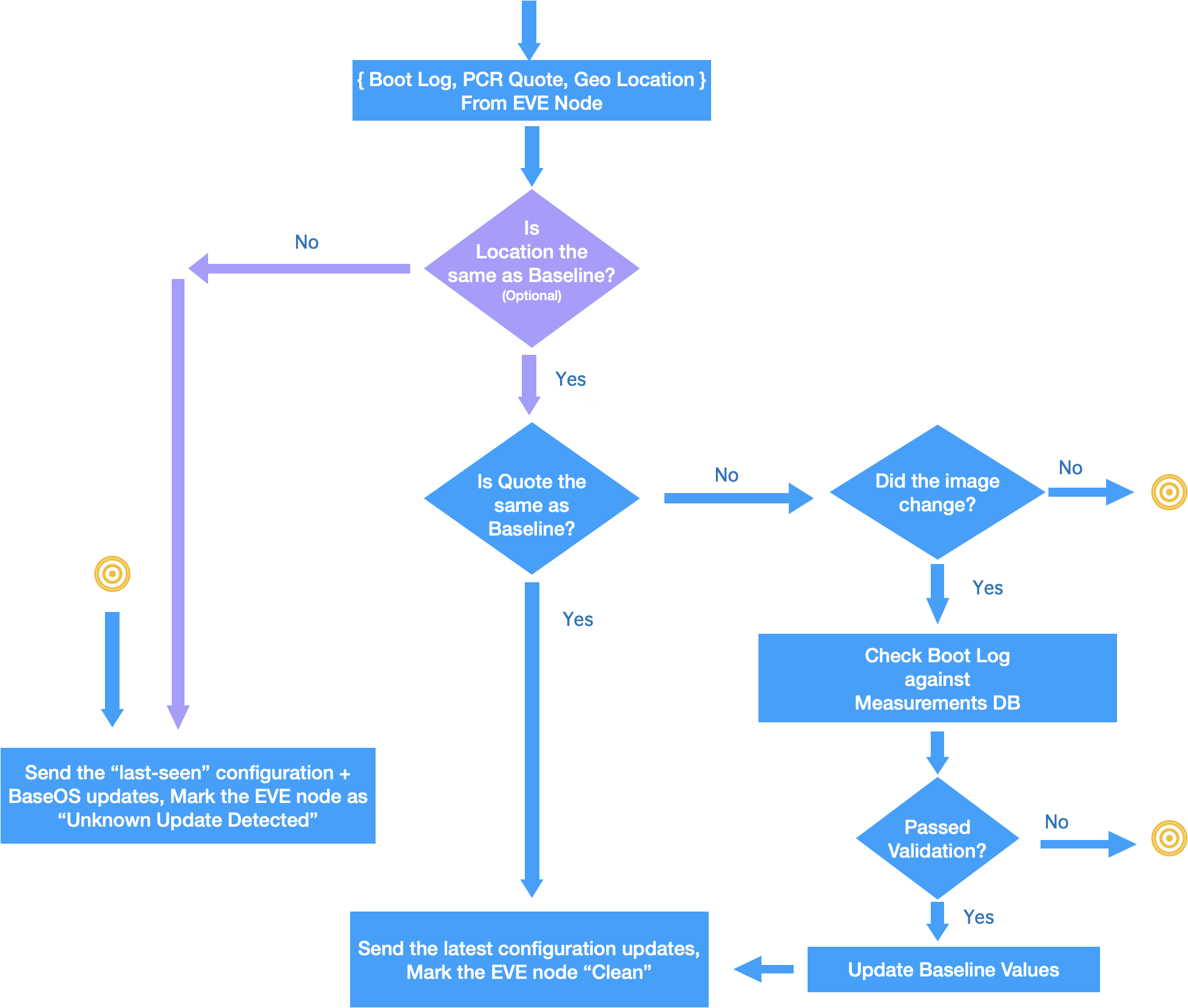
- After normal reboot operation of EVE, EVC checks PCR Quote against the baseline value. If there is a change, the edge-node is marked as “UUD”. If "Location-Lock" feature is enabled and the location of the EVE node has changed, EVE node is marked "UMD"
- After EVE software upgrade, it is expected that the baseline value will change for the PCR values. However, after comparing the reported values with the expected values(since EVC knows about the new image version and its hash values), EVC makes a decision: If the reported values match, the baseline for the EVE node is updated. If they don’t, it is a UUD detection. Optionally, if administrator enables “Location-Lock” feature, Geo-Location of the device will also be included in the checks, before sending the latest configuration.
- If edge-node is in “UUD” or "UMD" state, only the “last-seen” EVE configuration, along with the latest baseOS configuration is sent as config request response, all other new configuration items will be omitted in config response. This is to protect any new sensitive images/credentials from getting exposed to the compromised device. Here "last-seen" refers to the configuration last received by EVE from EVC.
- If EVE node is not in “UUD" or "UMD" state, all the latest configuration items are included.
- Frequency of attestation: EVE node will be required to periodically attest itself via attestation requests. The interval is fixed to be every 4 hours, or whenever the device connects back to the cloud again, or after the next reboot, whichever is earlier. This 4 hours is a tentative interval, and can be changed based on deployment requirements.
- If EVE reboots with a different software image from the configured version, EVC should be able to detect as quickly as possible and force attestation. To this effect a new token is introduced, called "Integrity Token". This token is a random nonce that will be stored in EVE under an encrypted folder. The master-key to decrypt this folder will be sealed against the TPM PCRs. Therefore, if EVE reboots with a different software, unsealing of this key will fail, and hence the new software will not be able to recover the Integrity Token inside it.
- This token is sent during attestation requests, and if the attestation is successful, the provided token value is locked against the EVE node.
- Every configuration request from EVE will include this Integrity Token. If there is a token mismatch, HTTP code 403 - Forbidden will be sent to the device as the response, indicating that device should do re-attestation.
Fig 2. Overview of Remote Attestation Flow in EVC
...
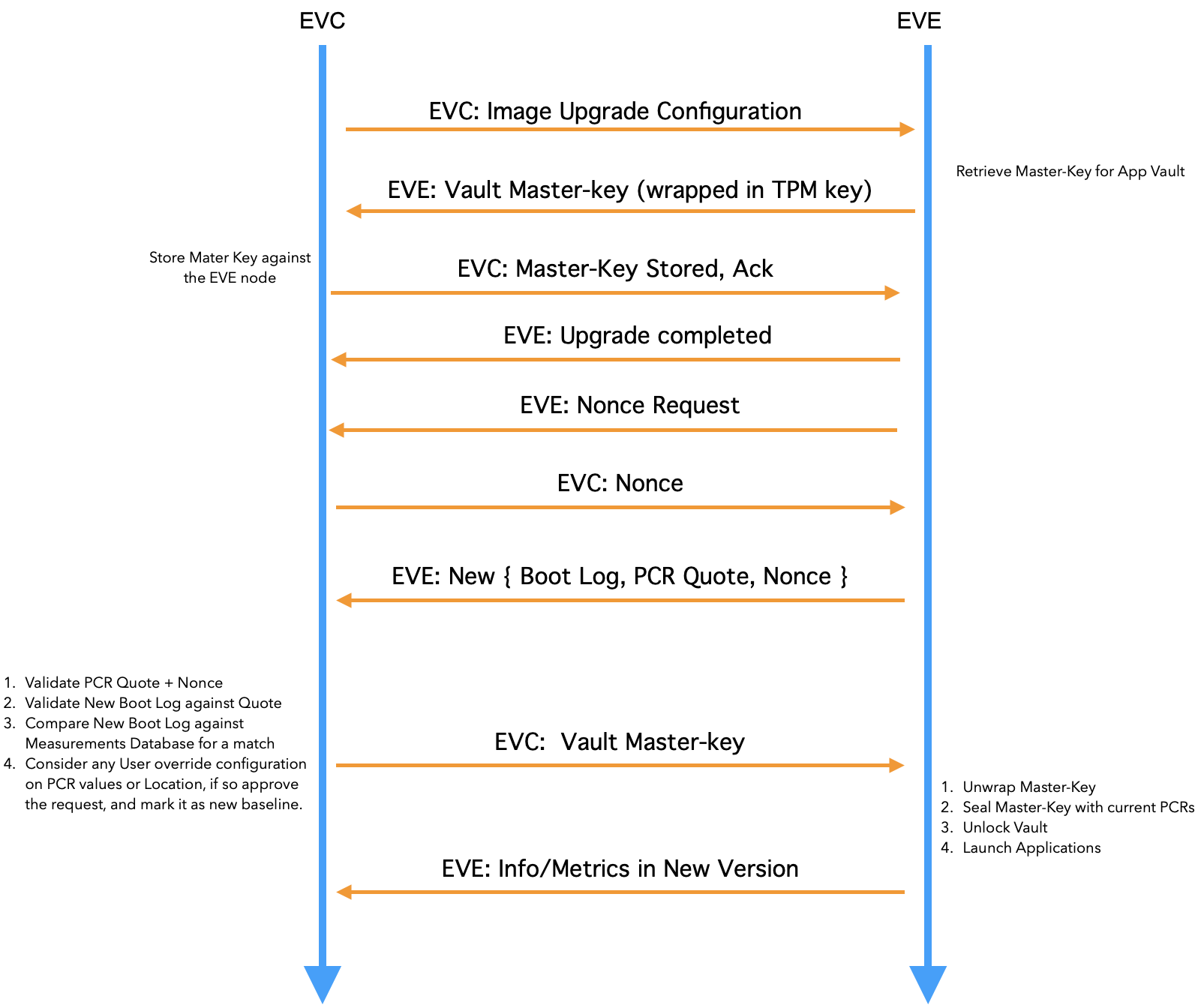
- EVE encrypts the master-key of the vault using a TPM-based key, and sends it to EVC. EVE can send this information when the master-key is created for the first time, and also can include this in the periodic info message. Sending this in periodic info message also provides additional facility of rotating the key if required.
- After the upgrade, the EVE software presents the new Event Log, along with the PCR Quote. As mentioned earlier, the PCR Extend operations are recorded in a table called TPM Event Log Table. This is sometimes also called the Boot Log.
- First, EVC repeats the transactions mentioned in the Event log, and the final PCR as computed from the Event Log should match the PCR Quote. If they don’t match, then Event Log can’t be trusted(say it was manipulated), and the EVE node is marked as UUD. Please note: Event Log is stored in system memory and PCR Quote is generated by TPM. So PCR quote is the source of truth, pinned to HRoT.
- Secondly, if PCR Quote matches the Event Log, then Event Log entries are compared between old Event Log and the new Event Log, and the differing entries are extracted
- EVC maintains a central database of all the supported EVE software images, and their hash values, indexed with the EVE image version tag
- EVC also maintains a central database of all the BIOS firmware images, their signatures, and the certificate provided by the BIOS vendor for validating the signatures, indexed by a combined tag of BIOS version string + Manufacturer
- The differing values are compared against acceptable values stored against the given image version. Additionally, If admin has enabled “Location-Lock” feature, additionally the geo-location reported by the device is checked as well. The Geo-location reported by the device can be trusted if the software state (established through PCR quote) can be trusted.
- If the PCR quote and the optional Geo-Location check pass, the encrypted master-key is given back to the EVE node. EVE decrypts the master-key, and unlocks the vault with the master-key. The master-key is now sealed into the TPM, against the current PCR values.
- User will have an option to override the attestation decision taken by EVC, through a configuration in EVC portal, against the EVE node
Fig 3. Flow Overview of flow of events during Secure Software Update
Updated EVE Startup
...
State Transition
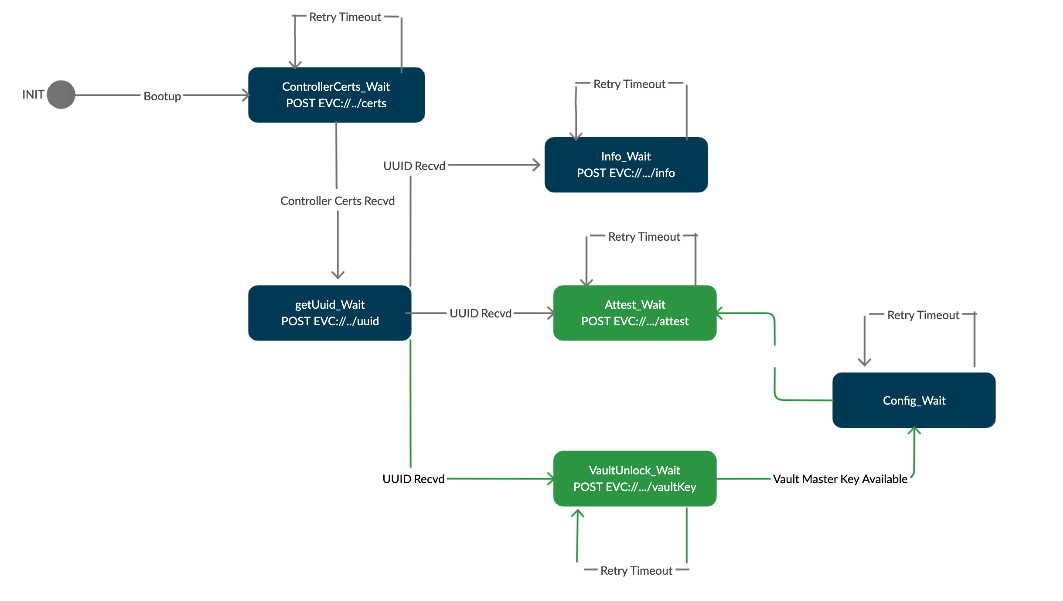
Fig 4. State Diagram for EVE Startup, with Attestation enabled
Module Level Interaction - Startup Sequence
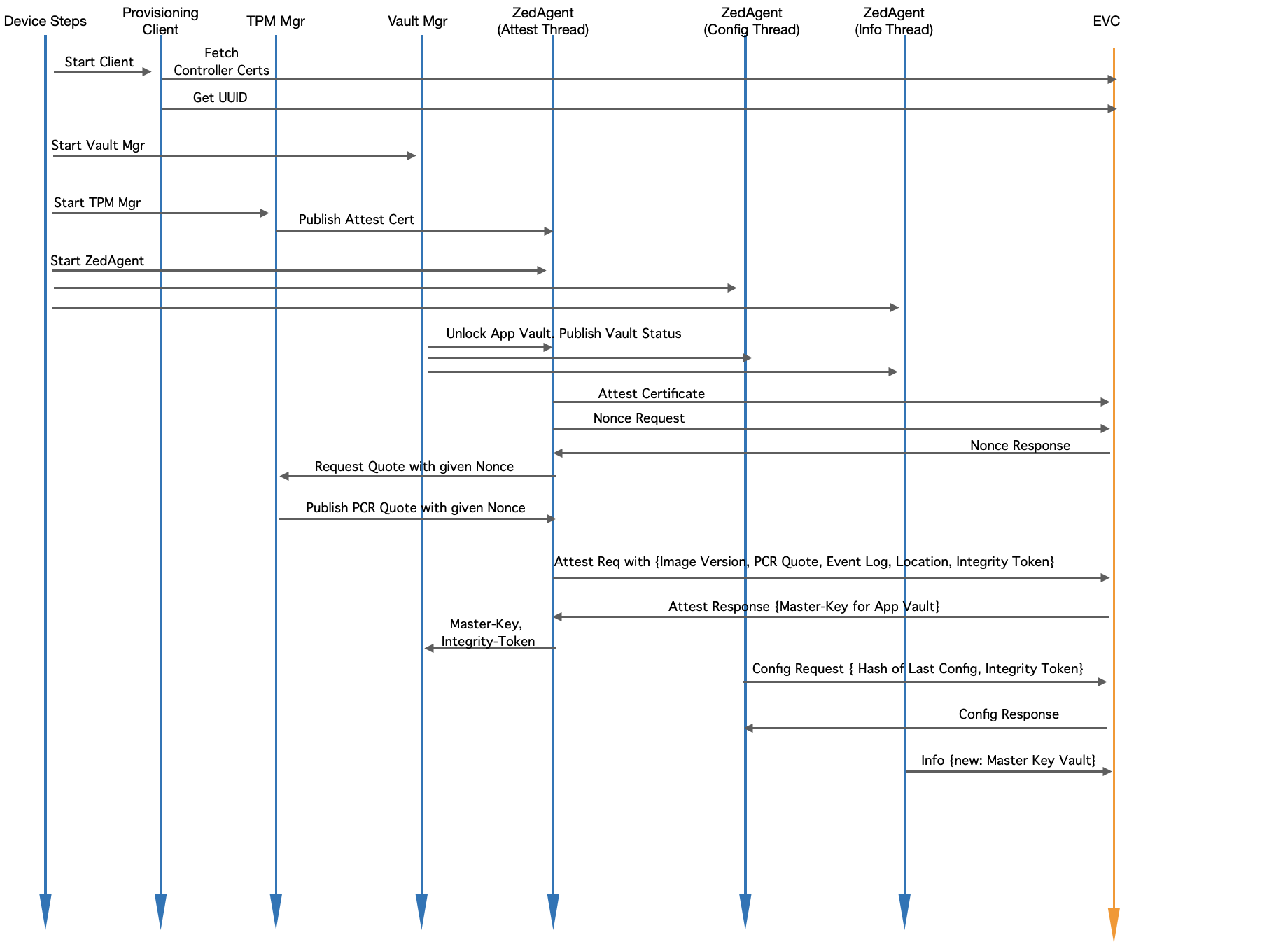
Fig. Module Level Interaction in EVE - Startup Sequence
Managing Firmware Upgrades
...